The study of matter
Chapter 1: Waves
Objectives: (what you will learn)
1)understanding Waves
2)reflection of waves
3)refraction of waves
4)diffraction of waves
5)interference of waves
6)analysing sound waves
7)analysing electromagnetic waves
Understanding Waves:
1.A wave is a traveling disturbance from a vibrating or oscillating source.
2.A wave carries energy along with it in the direction of its propagation.
3.A wave is a mean of energy transfer through vibration.
Waves:
Transverse Wave >>
Particles in the medium vibrate in a direction perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. Perpendicular = 90o to the line of direction.
Longitudinal Wave >>
Particles in the medium vibrate in a direction parallel (0o to line of direction) to the direction of wave propagation. Examples: wave in a slinky spring sound wave
Surface Waves >>
This is both transverse waves & longitudinal waves mixed in one medium. Examples: earthquake or seismic wave shear wave in a slinky spring
Wavefront :
A surface on the wave where all particles vibrate in phase (coming together to the same level).
Oscillations :
Vibration or oscillation of particles in a medium is like oscillation of simple pendulum or loaded spring.
Complete Oscillation >>
Complete cycle; e.g. motion from A to B & back to A.
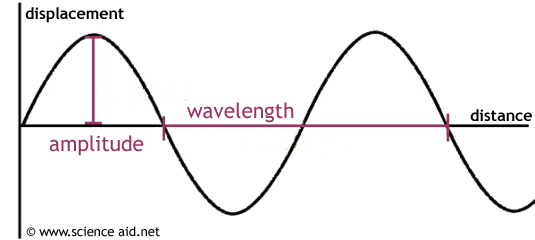
Amplitude, a >>
Maximum displacement from equilibrium position that is halfway between crest (high) & trough (low).
Period, T >>
Time taken for a complete oscillation.
Frequency, f >>
Number of complete oscillation in one second;
f = 1/T
Speed of wave, v >>
Distance traveled by wave per second, v = fλ
Free Oscillation >>
Occurs when a system oscillates without any external force acting on it.
Natural Frequency, fn >>
Frequency of a free oscillation.








0 comments:
Post a Comment